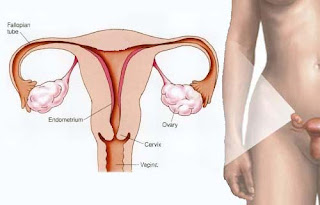
Ovaries
The ovary is a gland located on the right and left you womb. These ovaries that produce eggs (ova) as a new individual seedlings. Women in his life has about 60,000 ova released one by one every month and quit after the egg out, this is termed the menopause. In some circumstances, not all of these egg cells mature, so only about 400 ova there for a woman's life span. The mature ova will be removed from the ovaries to go into the uterus and ready to be fertilized. In addition to producing ova, the ovaries also produce hormones that are important to women, the hormone estrogen and progesterone, Which are vital for proper reproductive function.
Fallopian Tubes
Is the channel that connects the ovary to the uterus. This Fallopian tube extending from the ovary to the uterus. Funnel-shaped with a length of about three inches. This tube will carry the egg, so that fertilization occurs, which will then be placed in the uterus. Oviduct is located in the pelvis from the abdominal cavity with each tube is the union of the upper uterus. After Ova removed from the ovary, the tube which will move the ovum with the aid of fine feathers found on the surface of this tube.
Uterus
Uterus (Womb) is a place where the fertilized egg (zygote) is planted, where maturation, nutrition, and also the development until the birth process. Located in the pelvic cavity behind the bladder and in front of the large intestine. The uterus is usually tilted to the front with a ninety-degree angle toward the vagina, although only about 20% of women who have a uterus tilted back. The uterus has three layers: peritoneum (outer layer), miometrium (middle layer), and endometrium (inner lining). The uterus is coated with a network that could change during the menstrual cycle, because the influence of hormones produced by the ovaries. During pregnancy, the uterus stretches in length from three to four inches in order to accommodate the size of the baby to grow. During this period, the muscle wall increased two to three. Uterus shrinks back to half-pregnant weight before a week-old baby. At one month old baby, the uterus can be as small as when it first came out eggs from the ovaries.
Endometrium
The endometrium is the innermost layer of the uterus and place attached to the fertilized ovum. The endometrium lining found inside the blood vessels that are useful for delivering nutrients to these layers. When the fertilized ovum (called fertilization) stuck to the endometrial lining (implantation), the ovum will be connected with the parent body with placentas that in connection with the umbilical cord in infants.
In a phase in which the ovum is not fertilized by sperm, then kurpus luteum (the ovary) will stop producing the hormone progesterone and transforming into the corpus albikan that produce less hormone followed disintegrate layer has thickened endometrium, because the hormones estrogen and progesterone have stopped production. In this phase of the decay process occurs uterine wall, usually called menstruation.
Vagina
This channel connects the structure of the internal reproductive organs with your external genitalia. It had ended at the base of the cervix and is the entry point to the penis during sex as well as the final way out baby when born. Vagina, which is roughly two and a half to four inches, has a muscular wall with lots of blood vessels. This wall became straight when a woman is aroused because of the additional blood is pumped here. So in this case the vagina has three functions: as a container for the penis during sex; as a place to bleed during menstruation, and as a way for baby to pass through at birth.
June 18, 2010
Under Womens Reproductive
Label:
Endometrium,
Fallopian Tubes,
Ovaries,
Uterus,
Vagina,
Womb,
Womens Genitalia,
Womens Reproductive